파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영을 이용한 안구생체계측과 백내장수술 후 굴절력 예측의 비교
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Swept-source Optical Coherence Tomography Biometer and Partial Coherence Interferometer
Article information
Abstract
목적
백내장안에서 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영기계인 Argos와 부분결합간섭기계인 IOL Master® 500의 생체계측치를 비교하고, 백내장수술 후 굴절력 예측의 정확성을 비교해보고자 한다.
대상과 방법
백내장수술을 위한 검사를 받은 221안을 대상으로 Argos와 IOL Master® 500을 이용하여 안축장길이(axial length), 전방깊이(anterior chamber depth, ACD), 각막굴절률(K)을 측정하여 비교하였다. 수술 한 달 후 실제 굴절력과 예측굴절력을 이용한 절대굴절오차를 구하여 술 후 굴절 예측의 정확도를 비교하였다.
결과
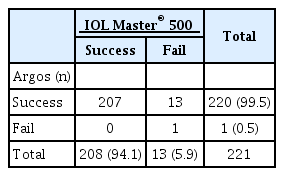
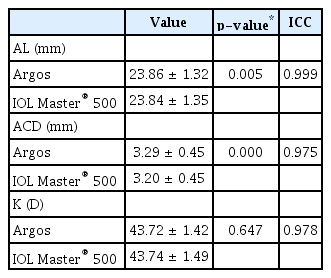
221안 중 13안은 IOL Master® 500으로 측정이 되지 않았으나, Argos로는 생체계측이 가능하였으며, 두 장비 모두에서 측정이 불가한 경우는 1안이었다. 측정이 불가했던 14안을 제외한 207안에서 두 장비로 측정한 생체계측값들은 급내상관계수(intraclass correlation coefficient, ICC) 및 Bland-Altman plot에서 높은 일치도를 보였다(ICC AXL=0.999, ACD=0.975, K=0.978). 안축장길이 및 전방깊이는 Argos로 측정한 경우가 IOL Master® 500으로 측정한 경우보다 유의하게 길었으나(p=0.005, p=0.000) 각막굴절률은 유의한 차이가 없었다(p=0.647). 두 장비의 수술 후 굴절력 예측에 대한 절대굴절오차는 통계적으로 유의한 차이가 없었다(p=0.087).
결론
Argos는 IOL Master® 500과 생체계측값의 높은 일치도를 보이면서도 계측값의 획득률이 더 높았다. 또한 통계적으로 동등하며 우수한 수술 후 굴절예측력을 보여주었다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
To compare the ocular biometry and postoperative refractive outcomes using two devices; the swept-source optical coherence tomography biometer (Argos) versus the partial coherence interferometer (IOL Master® 500, Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany).
Methods
The axial length (AL), anterior chamber depth (ACD) and keratometry (K) in 221 cataract eyes were measured with Argos and IOL Master® 500. One month after surgery, refraction of the respective eyes was conducted and the mean absolute error (MAE) calculated for analysis of the refractive outcomes.
Results
Measurement was not possible in 13 eyes with the IOL Master® 500 but was possible with Argos. Measurement was not possible in one eye with either biometer. Agreement in measured ocular biometry between the two devices by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland-Altman plot (ICC AXL = 0.999, ACD = 0.975, K = 0.978) was excellent. The AL and ACD measured with Argos were significantly longer than measured with IOL Master® 500 (p = 0.005, p = 0.000). The MAE showed no significant difference between the Argos and IOL Master® 500 (p = 0.087).
Conclusions
The measurement of ocular biometry was better in Argos than in IOL Master® 500. The accuracy of the intraocular lens power calculations of Argos was clinically acceptable and compatible with a conventional device.
다초점인공수정체 및 난시교정인공수정체 등이 대중화되면서 백내장수술은 단순한 백내장의 제거가 아닌 굴절교정 수술로서 받아들여지고 있으며, 이에 따라 더 정확한 생체계측을 위한 새로운 측정 방법 및 장비들의 관심도가 높아지고 있다.
인공수정체의 도수 계산을 위해 기존에 널리 사용되고 있는 부분결합간섭(partial coherence interferometry)의 원리를 이용한 IOL Master® 500 (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany)은 780 nm 파장의 적외선 광선을 이용하여 안축장 길이, 각막굴절률, 전방 깊이 등의 생체정보를 계측하고, 이를 기반으로 하여 인공수정체 도수를 계산한다[1,2]. 최근 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계(swept source optical coherence tomography)에 기반한 장비들이 소개되어 사용되고 있는데, 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계는 1,050 nm대(70 nm bandwidth)의 파장 영역을 이용함으로써 높은 투과성을 이용하여 안구 후부 구조물에 대한 더 정확한 정보를 얻고 매질혼탁으로 인한 산란에 영향을 덜 받는 것으로 알려져 있다[3,4]. Argos (Suntec, Inc., Nagoya, Japan)는 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계에 기반한 장비로서 안축장의 길이를 각 분절에 부합하는 굴절지수(refractive index)를 이용하여 분절의 길이를 측정하고 각각의 길이를 더하는 방식으로 계산하여 정확성을 높이고 있으며, 이에 따라 Barrett universal formula 등 최근 발표된 여러 가지 4세대 인공수정체 계산식을 사용할 수 있는 장점이 있는 장비로 소개된 바 있다[5].
파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계를 이용한 IOL Master® 700 (Carl Zeiss) [6,7], OA-2000 (Tomey, Nagoya, Japan) [8], Argos [4,5] 등과 부분결합간섭 원리를 이용한 IOL Master® 500의 생체계측값을 비교한 연구들이 진행되고 있다. 다만, 아직 국내에는 Argos와 IOL Master® 500의 생체계측값을 비교하고 수술 후 굴절력 예측의 정확도를 비교한 연구가 보고된 바 없다. 이에 본 연구에서는 Argos와 IOL Master® 500으로 측정한 안축장 길이, 전방깊이, 각막곡률의 일치도를 분석하고, 아울러 수술 후 실제굴절력과 예측굴절력의 차이에 대한 두 장비 간의 정확도를 비교하고자 하였다.
대상과 방법
2018년 4월과 2018년 10월에 제주대학병원 안과에 내원한 환자 중 백내장수술을 원하여 백내장수술을 위한 안구 생체 검사 진행에 동의하였던 환자를 대상으로 후향적 의무기록 분석을 시행하였다. 백내장수술을 위한 일반검사 중 생체계측을 위한 검사로 IOL Master® 500과 Argos를 같은 날 동일한 조건으로 촬영하였고, 양안 모두 검사하였다. 이전에 백내장수술을 받은 환자나 각막혼탁이 심한 경우, 빛이 거의 통과하지 못하리라 판단되는 심한 과숙 백내장이 있는 경우, 또는 망막 질환을 갖고 있는 경우는 대상에서 제외하였다. 본 연구는 헬싱키선언을 준수하였으며, 제주대학병원 의학연구심의위원회(Institutional Review Board, IRB)의 승인하에 진행되었다(승인 번호: 2019-09-006).
모든 환자에서 성별, 연령, 과거력을 조사하고, the Lens Opacities Classification System (LOCS) III [9]에 따른 백내장 정도를 조사하였다. 두 장비의 비교를 위한 생체계측은 안축장길이(axial length, AL), 전방깊이(anterior chamber depth, ACD), 평균 각막곡률(Keratometry, K)을 이용하였고, 이들의 일치도를 분석하였다. 이후 실제로 백내장수술을 진행한 환자들 중 수술 후 1개월째 굴절검사를 진행하여 구면(spherical)값에 원주(cylindrical)값의 절반을 더한 실제 굴절오차(refractive error, RE)를 구하고, 두 장비의 예측굴절오차와 실제굴절오차 차이의 절대값(절대오차 = |real RE – predictive RE|)의 평균(mean absolute error, MAE)을 각각 구하여 비교하였다. 예측 굴절값은 Haigis 공식과 Tecnis® ZCB00 (AMO, Santa Ana, CA, USA)을 기준으로 계산하였는데, 본 연구에서는 전방깊이를 두 장비의 계측 비교값으로 이용하였기 때문에 이를 반영하는 Haigis 공식을 예측 굴절값을 구하는 데 이용하였고, 안구의 특수성에 의해 실제 수술에 다른 공식값을 참고하여 수술하였더라도 수술 후 굴절력을 예측한 값은 동일하게 Haigis 공식을 이용한 값으로 비교하였다.
통계분석은 SPSS statistics ver. 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)을 사용하였으며, 급내상관계수(intraclass correlation coefficient, ICC)와 Bland-Altman plot을 구하여 일치도를 분석하였다. 각 계측값이 두 장비에서 차이가 있는지에 대해 대응표본 t-검정을 이용하였고, 계측값의 경향성에 대해서는 Pearson 상관계수를 이용하였다. 예측값 절대오차의 평균(MAE)의 비교는 각 장비에서 예측한 값의 오차가 어느 장비에서 더 0에 가까운지를 검정하기 위하여 독립표본 t-검정을 이용하였다. 통계적 유의수준은 0.05로 하였다.
결 과
총 129명 221안에 대해 분석하였다. 대상의 평균 연령은 68.9 ± 12.1세이고, 남자 58명, 여자 71명이었다. 221안 중 Argos에서 측정이 가능했지만 IOL Master® 500에서는 측정이 되지 않았던 눈은 13안이었으나, IOL Master® 500에서 측정이 가능했으나 Argos에서 측정이 되지 않은 경우는 없었다. 두 장비에서 모두 측정이 되지 않은 경우는 1안이었다(Table 1).
두 장비 모두 측정이 가능했던 207안의 안축장의 길이의 평균은 Argos에서 23.86 ± 1.32 mm, IOL Master® 500에서 23.84 ± 1.35 mm로 유의하게 Argos에서 평균 0.02 mm가량 더 길게 측정되었다(p=0.005). 전방깊이의 평균은 Argos에서 3.29 ± 0.45 mm, IOL Master® 500에서 3.20 ± 0.45 mm로 유의하게 Argos에서 더 길게 측정되었다(p=0.000). 각막굴절률의 평균은 Argos에서 43.72 ± 1.42 diopters (D), IOL Master® 500에서 43.74 ± 1.49 D로 유의한 차이는 없었다(p=0.647) (Table 2).
두 장비를 이용한 생체계측의 급내상관계수는 안축장길이 0.999, 전방깊이 0.975, 각막곡률 0.978이었고(Table 2), Bland-Altman plot에서도 계측값들의 높은 일치도를 보였다(Fig. 1-3). 특징적으로 안축장의 길이가 짧을수록 Argos로 측정한 안축장의 길이가 IOL Master® 500에서 측정한 것보다 더 길게 측정되었다는 것인데(상관계수: -0.411, p=0.000), 선형회귀식은 Y=-0.019X +0.468 (ɛ=0.468, p=0.000; ß=-0.019, p=0.000)으로, 안축장의 길이가 24.63 mm 미만일 때는 Argos가 측정한 안축장이 IOL Master® 500으로 측정한 안축장보다 약간 길게 측정되고, 24.63 mm 이상일 때는 Argos에서 측정한 안축장이 IOL master 500에서 측정한 것보다 약간 짧게 측정되는 경향이 있었다(Fig. 1). 실제로 백내장수술을 진행한 경우 중 Tecnis® ZCB00 (AMO)을 삽입한 눈이 126안으로 MAE는 Argos에서 0.531 ± 0.524 D, IOL Master® 500에서 0.477 ± 0.450 D였고, 두 값 간의 유의한 차이는 없었다(p=0.087).
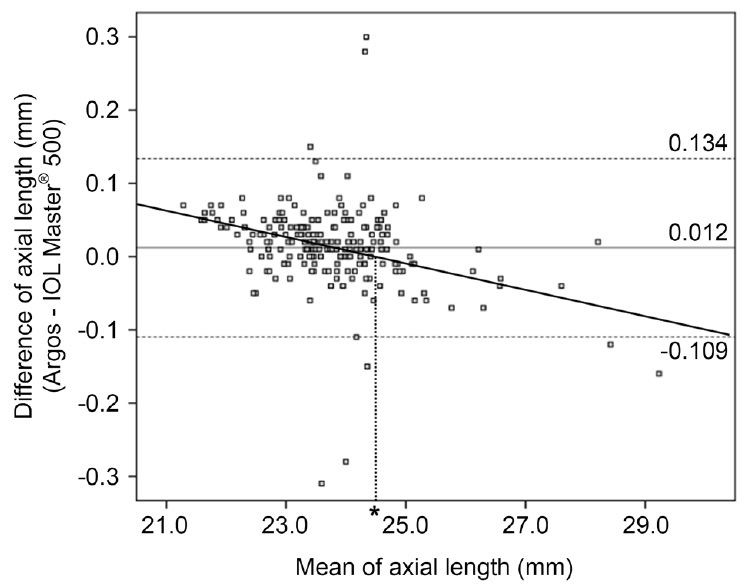
Bland–Altman plot of axial length (AL) using Argos and IOL Master® 500 (Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Jena, Germany). The solid line indicates the mean difference (0.012 mm). The dashed lines indicate the 95% limits of agreement (-0.109 mm, 0.134 mm). There was a significant negative correlation between the mean AL of the two biometers and the difference of AL (r = -0.412, p = 0.000). Bold line indicates Y = -0.019X+0.468, ɛ=0.468 (p = 0.000), ß = -0.019 (p = 0.000) by linear regression analysis. The ALs measured by Argos which was less than 24.63 mm (*) tended to be longer than ALs measured by IOL Master® 500.
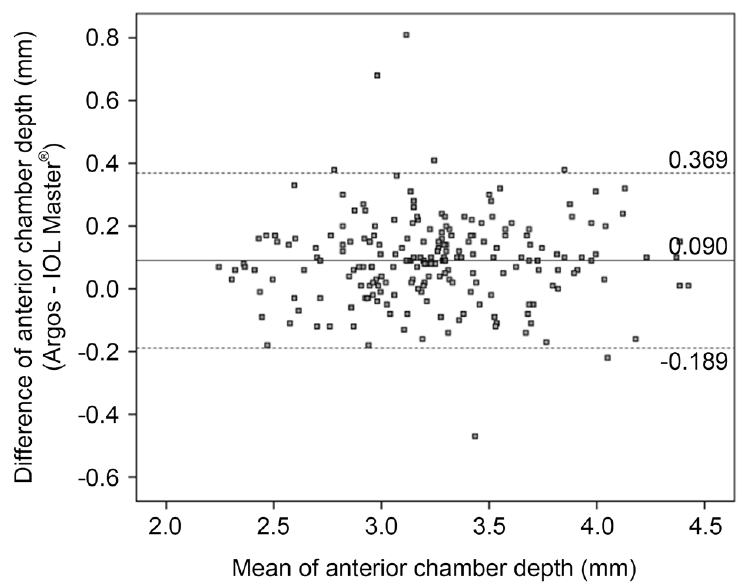
Bland–Altman plot of anterior chamber depth using Argos and IOL Master® 500. The solid line indicates the mean difference (0.090 mm). The dashed lines indicate the 95% limits of agreement (-0.189 mm, 0.369 mm).
고 찰
안축장길이의 획득률(acquisition rate)은 Argos에서 99.5% (220안/221안), IOL Master® 500에서 94.1% (208안/221안)이었다. 안축장의 길이, 전방깊이, 각막곡률값은 모두 두 장비에서 높은 일치율을 보였으나 안축장의 길이는 미세한 차이지만 Argos에서 측정한 값이 유의미하게 더 길었고, 전방깊이 또한 Argos에서 측정한 값이 IOL Master® 500으로 측정한 값보다 유의미하게 길게 측정되었다. 각막곡률은 유의한 차이가 없었다. 특히 안축장의 길이가 24.63 mm보다 길수록 Argos에서 측정된 안축장의 길이가 IOL Master® 500에서 측정된 값에 비해 더 짧게 측정되는 경향이 있었다. 본 연구에서 환자들의 평균 안축장은 23.85 mm로, 두 장비의 안축장 측정치의 분기점이 되는 24.63 mm보다 다소 짧았기 때문에, Argos로 측정한 안축장의 평균 길이가 IOL Master® 500으로 측정한 안축장의 평균 길이보다 0.02 mm 길게 측정된 것으로 판단된다. 수술 후 1개월째에 측정한 굴절력과 수술 전에 예측한 굴절력 차이의 평균을 비교했을 때 Argos로 예측한 값이 IOL Master® 500으로 예측한 값과 실제 값과의 오차는 유의한 차이가 없었다.
생체계측, 특히 안축장길이의 획득률은 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계를 이용한 장비에서 92.5-100%, 부분결합간섭계를 이용한 장비에서 64-87.3%로 다양하게 보고되고 있으며[4,5,8,10], 차이가 큰 이유는 대상의 선정 및 제외 조건이 각 연구마다 다르기 때문인데, 이런 이유를 감안하더라도 대체적으로 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계를 이용한 장비에서 부분결합간섭계를 이용한 장비보다 월등히 높게 보고되고 있고, 본 연구에서 또한 Argos를 이용했을 때 획득률이 높았다. 두 장비 모두에서 값을 얻는 데 실패한 1안의 경우 수정체겉질과 핵이 모두 LOCS III [9] 기준으로 4단계 이상의 심한 백내장 상태였다. Argos에서는 값을 얻는 데에 성공하였으나 IOL Master® 500에서는 실패했던 13안을 살펴보면 후낭하 및 전낭하백내장이 심했던 경우가 10안이었고, 나머지 3안은 겉질 또는 핵 백내장이 LOSC III 기준 3단계 이상의 심한 백내장이었다. 각막혼탁, 백내장, 유리체혼탁 등의 매체 혼탁이 있는 경우에도 1,050 nm 파장대를 이용한 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계는 기존의 800 nm 파장대를 이용한 빛간섭단층촬영(frequency domain optical coherence tomography)보다 더 우수한 투과성과 영상의 질을 제공하는 것으로 알려져 있다[11]. 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계, 부분결합간섭계, 저간섭성반사계를 이용한 생체계측장비를 비교한 Shammas et al [4]의 연구에도 과숙백내장(white cataract)을 가진 두 증례에서는 세 장비 모두 측정 불가하였지만, 5단계의 핵백내장과 후낭하백내장이 동반된 증례들과 4단계의 수정체겉질변화와 3단계의 후낭하백내장이 동반된 몇 개의 증례에서 부분결합간섭계 및 저간섭성반사계를 이용한 생체계측장비는 안축장길이를 측정할 수 없었고, 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계를 이용한 생체계측장비는 안축장을 측정할 수 있었다고 보고하였다.
IOL Master® 700, OA-2000, Argos 등의 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계를 이용한 생체계측장비와 부분결합간섭계를 이용한 IOL Master® 500의 생체계측값들의 일치율은 매우 높은 것으로 보고되었다[4-8]. 본 연구에서도 두 장비에서 측정한 생체계측값들은 모두 높은 일치율을 보였지만, 대응 표본으로 평균을 비교하였을 때 안축장의 길이와 전방깊이는 Argos에서 더 길게 측정되는 결과를 얻었다. 또, 특징적으로 안축장의 길이가 길수록 Argos에서 측정한 값이 IOL Master® 500보다 작게 측정이 되었다. 이것은 Higashiyama et al [5]이 보고한 내용과 일치하는 부분으로 짧은 안축장 그룹(Short AL)과 중간 안축장 그룹(Intermediate AL) 그리고 긴 안축장 그룹(Long AL)을 나누어 안축장 길이를 비교했을 때 Short AL에서는 Argos로 측정한 안축장의 평균값이 더 길었으나, Long AL에서는 Argos로 측정한 안축장의 평균값이 더 짧았다. Argos는 네 분절(segment)의 분절굴절지 수(segmental refractive index)를 각각 적용하여 길이를 구하여 더하는 방식으로 안축장 길이를 측정하지만 IOL Matser® 500은 하나의 굴절지수(single refractive index)를 이용한다. 한 연구에서는 성인의 안축장의 길이의 차이는 대부분 유리체강의 길이에서 차이가 난다고 보고하였다[12]. 즉, 유리체강에 적용되는 굴절지수와 IOL Master® 500의 단일 굴절지수 차이에 의해 안축장의 길이가 길어질수록 Argos에서 측정한 길이보다 IOL Master® 500에서 측정한 길이가 더 길어지게 되는 결과가 나온 것이라 추정된다. 그러나 이러한 결과는 결국 두 장비 중 하나의 안축장길이 측정 결과의 신뢰도가 떨어지는 것을 의미하고 이러한 원인에 대한 후속연구 및 보완이 필요할 것이다.
전방깊이를 측정하는 방법에 있어 IOL Master® 500은 부분결합간섭을 이용하는 것이 아닌 각막과 수정체의 세극조명(lateral slit-illumination)을 이용하여 샤임플러그 원리(scheimpflug principle)로 전방깊이를 측정하는 방식을 취하고 있다[13]. Akman et al [6]과 Yoo et al [10]의 연구에서 IOL Master® 700의 원리는 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영 기법을 이용하여 전방깊이의 단면 영상을 분석하는 것으로, 1,050 nm 긴 파장 레이저를 사용하며, 6개의 0°, 30°, 60°, 90°, 120°, 150°의 회전 단면들에서의 측정치를 얻기에 전방깊이가 IOL Master® 500로 측정한 것보다 유의하게 더 짧게 측정되었음을 보고하였다. Omoto et al [14]의 연구에서는 Argos와 IOL Master® 700의 생체계측값과 수술 후 굴절력의 예측 오차를 비교하였는데, Argos로 측정한 전방깊이가 IOL Master® 700보다 유의하게 길게 측정되는 것을 보고하였다. 위에서 언급한 바와 같이 Argos는 분절굴절지수를 사용하는 반면 IOL Master® 700은 당량굴절지수(equivalent refractive index)를 사용한다[14]. 결국 전방깊이의 차이는 측정방식과 굴절지수에 의한 것으로 추측할 수 있고, Argos에서는 IOL Master® 500이나 700보다 길게 측정되고 있다고 판단해 볼 수 있다. 또한, 위 연구에서는 중간안축장그룹(Medium ALs; 22.00≤AL<26.00 mm)과 긴안축장그룹(Long ALs; AL≥26.00 mm)으로 나누어 Haigis, HofferQ, SKR/T, Barrett Universal II 공식에 따른 두 장비의 절대오차 및 절대오차의 평균을 비교하였는데, 모든 공식에서 절대오차값은 IOL Master® 700과 비교하여 Argos에서 유의하게(p<0.001), 0에 가까운 값을 가졌고, 특히 Long ALs에서 절대오차의 평균(MAE)은 HofferQ와 SRK/T 공식하에 유의하게 Argos에서 더 작았다. 이것 또한 분절굴절지수와 당량굴절지수에 따라 유발되는 차이에 의한 결과로 해석해 볼 수 있고, Argos가 경쟁력 있는 수술 후 굴절력 예측을 제공하고 있음을 볼 수 있다.
본 연구에서 파장가변 빛간섭단층촬영계를 이용한 생체계측기(Argos)는 기존 부분결합 간섭계를 이용한 생체계측기보다 조금 더 우수한 획득률(99.5% vs. 94.1%)를 보였다. 두 장비로 측정한 생체계측값들은 서로 높은 일치도를 보였고, 또한 통계적으로 동등하며 우수한 수술 후 굴절예측력을 보여주었다. 그러나 안축장의 길이에 따라 미세하지만 유의미한 차이가 관찰되었기에, 추후 더 많은 환자군을 대상으로 한 세분화된 추가 연구가 필요하겠으며, 이를 통해 조금 더 정확한 수술 후 굴절력 예측이 가능해질 것으로 기대한다.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
장미리내 / Mirinae Jang
제주대학교 의학전문대학원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine