외상성 전방출혈 후 전방깊이의 단기 변화
Short-term Changes in Anterior Chamber Depth after Traumatic Hyphema
Article information
Abstract
목적
외상성 전방출혈 환자에서 수상 1달째까지의 전방깊이의 단기간 변화 양상을 분석해 보고자 하였다.
대상과 방법
2015년 10월부터 2019년 7월까지 본원에 내원한 외상성 전방출혈 환자 32명의 의무기록을 후향적으로 조사하였다. 이 중 1달 째까지 경과 관찰이 가능하였던 환자는 총 19명이었다. IOLMaster® 500을 통해 측정한 수상 직후 및 수상 1달째 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이와 그 차이를 각각 비교 분석하였다. 또한 육안상 전방출혈군과 미세전방출혈군 사이에 환측과 반대측 간의 전방깊이의 차이, 나이에 따른 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이의 차이의 상관성을 각각 추가적으로 비교 분석하였다.
결과
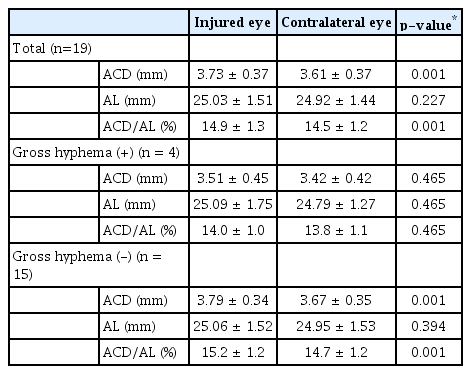
환자들의 평균 나이는 36.0 ± 14.2세였으며, 남자는 24명(75%)이었다. 수상 직후 환측의 전방깊이는 3.81 ± 0.38 mm로 반대측의 전방깊이 3.55 ± 0.43 mm에 비해 유의한 증가를 보였고(p=0.021), 수상 1개월 후 환측의 전방깊이는 3.73 ± 0.37 mm로 반대측의 전방깊이 3.61 ± 0.37 mm에 비해 여전히 유의한 차이를 보였다(p=0.001). 수상 직후 육안상 전방출혈군과 미세전방출혈군 사이에 환측과 반대측 간의 전방깊이, 전방깊이/안축장 길이의 차이는 유의한 다름을 보이지 않았다(p=0.951/0.981). 환측은 수상 직후 3.87 ± 0.40 mm의 전방깊이를 보였으나, 수상 1개월 후 3.73 ± 0.37mm로 유의하게 감소하였다(p=0.013). 수상 직후 고령일수록 유의하게 전방깊이의 차이가 커지는 경향이 있었다(R=0.387, p=0.018).
결론
전방출혈이 발생한 눈에서 반대측에 비해 수상 직후 유의한 전방깊이의 증가가 관찰되었다. 또한 이러한 증가는 수상 1달 후 감소하지만 여전히 반대측에 비해 유의하게 증가되어 있었다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
To analyze short-term changes in anterior chamber depth (ACD) immediately and 1 month after traumatic hyphema.
Methods
Thirty-two patients with traumatic hyphema treated from October 2015 to July 2019 were retrospectively reviewed. Nineteen were followed-up for 1 month. The ACDs were measured using an IOL Master 500 platform and the differences between the affected and contralateral eyes immediately after trauma and 1 month after treatment analyzed. The ACD differences between the affected and contralateral eyes of those with gross and microscopic hyphema and the correlations between the ACD differences of the two eyes were analyzed by age.
Results
The average age was 36.0 ± 14.2 years and 24 patients were male (75%). The ACDs of affected eyes were greater than those of contralateral eyes both immediately after trauma (3.81 ± 0.38 vs. 3.55 ± 0.43 mm; p = 0.021) and 1 month after trauma (3.73 ± 0.37 vs. 3.61 ± 0.37 mm; p = 0.001). The ACD gaps and ACD/axial length ratios (%) did not differ significantly between the injured and contralateral eyes of the gross and microscopic hyphema groups immediately after trauma (p = 0.951/0.981). The ACDs of affected eyes decreased 1 month after trauma compared to immediately after trauma (3.73 ± 0.37 vs. 3.87 ± 0.40 mm; p = 0.013). The ACD difference immediately after trauma increased significantly with older age (R = 0.387, p = 0.018).
Conclusions
The ACDs of eyes with traumatic hyphema increased significantly compared to those of the contralateral eyes immediately after trauma. The ACDs decreased after treatment but 1 month later were still significantly greater than the ACDs of the contralateral side.
외상 이후 발생한 출혈이 전방 내로 들어오는 것을 외상성 전방출혈이라 한다. 외상성 전방출혈은 시력 예후에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 흔한 안구 외상 중 하나로 재출혈, 이차성 녹내장, 각막 혈액 침착 등 추가적인 합병증으로 이어질 수 있어 주의가 필요한 질환이다. 안구에 충격이 가해지면 안압이 일시적으로 상승하게 되고, 수정체 홍채면(lens-iris diaphragm)이 후방으로 이동하면서 섬모체혈관에 손상이 생겨 전방출혈이 발생하게 된다.1 전방깊이는 각막의 상피세포 중앙부 전면부터 수정체전낭 중앙부 전면까지의 거리로,2 눈의 굴절력, 안압 등과 밀접한 연관이 있어 인공수정체 도수 결정, 녹내장 등의 연구에 있어 의미 있게 사용되는 지표이다.3 일반적으로 양안 전방깊이의 차이는 평균적으로 0.1 mm 미만의 차이를 보인다.4
외상성 전방출혈 환자에서 앞서 언급한 기전에 따라 수상 전에 비해 전방깊이가 깊어질 수 있을 것으로 예상해 볼 수 있다. 호주의 한 연구에서도 외상성 전방출혈이 있었던 환아들에게서 반대안에 비해 환측의 전방깊이가 유의하게 증가하였다고 보고된 바 있다.5 그러나 성인에서 이와 관련된 국내외의 연구는 필자들이 파악한 바로는 이제까지 진행된 바 없다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 외상성 전방출혈 성인 환자에서 수상 직후 및 수상 1달째 초기 전방깊이 변화를 분석해보고자 하였다.
대상과 방법
임상연구심의위원회의 승인 하에 2015년 10월부터 2019년 07월까지 안과에 외상성 전방출혈로 내원한 환자 32명의 32안을 대상으로 진료기록을 후향적으로 조사하였다(IRB number: GBIRB2022-230). 32명의 연구 대상자들은 공, 배드민턴채, 구타, 작업 중 수상 등 32명 전원 둔상에 의한 수상으로 내원하였고 항생제, 스테로이드 안약, 산동제, 안압 약을 통한 치료를 진행하였다. 산동제는 모두 cyclopentolate hydrochloride 계열 안약을 사용하였으며 평균 사용 일수는 8.1일, 1달 후 생체계측검사 시에 산동제를 사용 중인 환자는 없었다. 상기 환자 전원 전방깊이의 측정에는 광학적 생체계측 장비(optical biometry device)나 각막지형도 장비(corneal topography) 등이 사용되는데 본 연구에서는 이 중 정확성과 재현성이 비교적 높은 IOL Master® 500 (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany)을 이용해 전방깊이를 측정하였다.6 수상 전 안과 질환의 기왕력이 있거나 수상 후 망막박리, 외상성 백내장 등 안축장 길이나 전방깊이 측정에 영향을 줄 수 있는 질환이 동반된 환자들은 연구 대상에서 제외하였다. 수상 전 백내장수술을 받았던 경우, 검사에 협조가 잘 되지 않거나, 심한 백내장 등의 이유로 생체계측이 불가능한 경우, 개방안구손상이 있는 경우는 본 연구에서 제외하였다. 수상 직후 전방깊이의 변화와 회복 이후 전방깊이의 변화 양상을 비교하기 위하여 수상 직후 외래 내원 시의 양안의 전방깊이와 안축장 길이, 수상 한 달 후의 외래 내원 시의 양안 전방깊이와 안축장 길이를 계측하였다. 수상 1개월 후 생체 계측을 측정할 수 있었던 대상군은 총 19명이었다. 내원 시 최대교정시력, 안압을 측정하였으며 세극등현미경검사를 통해 육안 상의 전방출혈(gross hyphema)과 미세전방출혈(microscopic hyphema)로 구분하였고 Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) 기준에 따라 전방세포의 정도를 1-4단계로 측정해 전방 세포의 단계를 분류하였다.7
수상 직후 환측의 전방깊이가 유의하게 증가하는지를 확인하기 위해 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이를 비교하였고, 안축장 길이가 길어짐에 따라 전방깊이가 증가하는 것에 대한 보정을 위해 전방깊이/안축장 길이 비율(%)을 함께 비교하였다.8 수상 이후 변화한 전방깊이가 초기에 어떻게 변화하는지를 확인하기 위해 수상한 안의 수상 직후와 한 달 후의 전방깊이와 전방깊이/안축장 길이를 추가적으로 측정하였다. 수상 후 증가하였던 전방깊이가 회복되고 난 후 측정한 전방깊이와 반대안의 전방깊이를 비교하였을 때 유의한 차이가 있는지 확인하기 위해 수상 1달 후 수상한 안과 반대안의 전방깊이와 전방깊이/안축장 길이를 함께 비교하였다. 전방출혈의 정도에 따른 오차를 비교하기 위하여 세극등현미경상 육안 상의 전방출혈군과 미세전방출혈군에 대해서 따로 구분하여 전방깊이와 안축장 길이의 계측값을 비교하였다. 마지막으로 환자의 나이와 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이의 차이간의 상관성을 수상 직후와 수상 1달 후 각각 분석해 보았다.
통계 소프트웨어는 SPSS 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Armonk, NY, USA)을 이용하였다. 각 계측값 간의 비교는 Mann-Whitney test 또는 Wilcoxon signed rank test를 이용하였고, 상관성 분석은 Spearman’s correlation test를 이용하였다. 통계적 유의성은 p<0.05로 정의하였다.
결 과
연구대상자 중 남자는 24명(75%), 여자는 8명(25%)이었으며 평균 나이는 36.0 ± 14.2세였다. 수상한 안의 최대교정시력(logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution)은 0.59 ± 0.60, 전방세포의 단계는 3.0 ± 1.0, 안압은 13.4 ± 5.2 mmHg였다. 수상한 눈의 전방깊이는 3.81 ± 0.38 mm, 안축장 길이는 24.97 ± 1.34 mm, 전방깊이/안축장 길이는 15.3 ± 1.4%였다(Table 1).
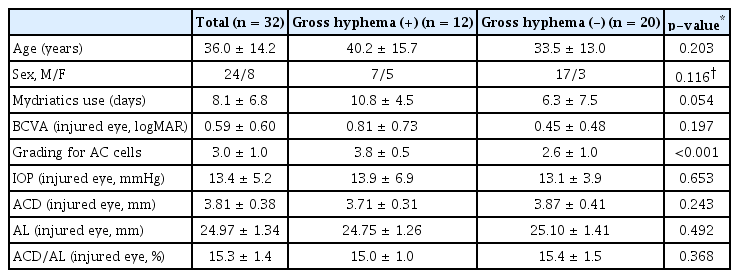
수상 직후 환측의 전방깊이 3.81 ± 0.38 mm는 반대측의 전방깊이 3.55 ± 0.43 mm에 비해 유의한 증가를 보였으나, 안축장 길이는 환측 24.97 ± 1.34 mm로 반대측 24.93 ± 1.27 mm로 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다(p=0.021/0.976). 전방깊이/안축장 길이는 15.3 ± 1.4%로 반대측 14.2 ± 1.6%와 유의한 차이를 보였다(p=0.012). 육안상 전방출혈군(gross hyphema+)과 미세전방출혈군(gross hyphema-)으로 나누었을 때도 수상한 안과 반대안의 안축장 길이(mm)는 유의한 차이가 없는 반면 전방깊이(mm)와 전방깊이/안축장 길이(%)는 유의한 차이를 보였다(gross hyphema+/-: 안축장길이, p=0.899/0.925; 전방깊이, p=0.029/0.041; 전방깊이/안축장 길이(%)-p=0.023/0.031) (Table 2). 또한 대상자 전체, 육안상 전방출혈군, 미세전방출혈군 사이에 환측과 반대측 간의 전방깊이의 차이, 전방깊이/안축장 길이(%)의 차이 모두 유의한 다름을 보이지는 않았다(p=0.951/0.981) (Fig. 1).
Comparison of ocular biometry between gross hyphema and microscopic hyphema subgroups at initial examination. (A) Difference of ACD at initial examination. (B) Difference of ACD/AL at initial examination. ACD = anterior chamber depth; AL = axial length.
수상한 안의 수상 직후와 수상 1개월 후의 계측값을 비교하였을 때 전방깊이는 수상 직후 3.87 ± 0.40 mm, 1개월 후 3.73 ± 0.37 mm로 유의한 감소를 보였다(p=0.013). 안축장 길이는 수상 직후 25.03 ± 1.52 mm, 1개월 후 25.03 ± 1.51 mm로 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다(p=0.948). 전방깊이/안축장 길이는 수상 직후 15.5 ± 1.23%, 1개월 후 14.9 ± 1.3%로 유의한 감소를 보였다(p=0.014) (Table 3).

Change of ocular biometry at an injured eye between initial examination and 1 month follow-up examination
수상 1개월 후 환측의 전방깊이는 3.73 ± 0.37 mm로 반대측의 전방깊이 3.61 ± 0.37 mm와 유의한 차이를 보였다(Mann-Whitney U test, p=0.001). 환측의 안축장 길이는 25.03 ± 1.51 mm로 반대측 24.92 ± 1.44 mm와 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았으나, 환측의 전방깊이/안축장 길이는 14.9 ± 1.3%로 반대측의 14.5 ± 1.2%와 유의한 차이를 보였다(p=0.227/0.001). 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이의 차이는 수상 직후 0.27 ± 0.24 mm였고, 수상 1달 뒤 0.12 ± 0.08 mm로 감소하였다(Table 4).
Comparison of ocular biometry between injured and contralateral eyes at 1 month follow-up examination
한편 환자의 나이와 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이의 차이의 상관성을 분석하였을 때, 수상 직후 고령일수록 유의하게 전방깊이의 차이가 커지는 것을 확인할 수 있었으나 이러한 상관관계는 수상 1달 후에는 유의하지 않게 변화하였다(R=0.387/-0.072, p=0.018/0.791) (Fig. 2).

Correlations between age and difference of ACD. (A) Correlations between age and difference of ACD at initial examination. (B) Correlations between age and difference of ACD at 1 month follow-up examination. ACD = anterior chamber depth.
또한 수상 직후와 수상 1개월 후 굴절값 측정이 가능하였던 14명의 14안을 대상으로 구면 대응치(spherical equivalent)를 비교 분석하였을 때, 수상 직후 구면대응치는 -2.1 ± 2.1 diopters (D), 수상 1개월 후 구면대응치는 -1.9 ± 2.1 D로 유의한 차이를 보이지 않았다(p=0.328).
고 찰
본 연구에서는 수상한 눈의 전방깊이가 반대측에 비해 수상 직후 유의하게 증가하고, 수상 1달째 환측 전방깊이가 수상 직후에 비해 유의하게 감소하지만, 반대측에 비해서는 여전히 유의하게 증가되어 있음을 보여주었다. 전방깊이를 안축장 길이로 나누어 비율로써 보정한 경우에도 마찬가지로 유의한 차이를 보였다. 다만 수상의 정도를 간접적으로 나타내는 지표인 육안상 전방출혈과 미세전방출혈 군으로 나누었을 때, 두 군 간 유의한 전방깊이의 차이는 보이지 않았다.
안구 둔상이 발생하는 경우, 손상과 관련된 안구의 압박으로 인해 안압의 일시적이면서 급격한 상승과 함께 앞방각의 후퇴가 보통 발생하고, 수정체 홍채면이 후방으로 이동하면서 섬모체혈관에 손상이 생겨 전방출혈이 발생하게 된다.1,5 이전 외상성 전방출혈 병력이 있는 소아를 대상으로 한 호주의 한 연구에서 환측의 앞방각 후퇴가 발생할수록 양안 전방깊이의 비대칭이 발생하며, 환측과 반대측의 안압의 비대칭이 심할수록 전방깊이의 비대칭 또한 심해진다고 보고하였다.5 전방출혈이 있는 소아의 경우 평균 50% 정도의 앞방각 후퇴가 발생하였다는 보고에 비해 성인의 경우에는 71-83%까지 높게 보고되고 있다.9,10 아마도 소아에서 성인에 비해 홍채 근부와 안구 조직 자체가 탄력성이 보통 더 크기 때문에 상대적으로 앞방각 후퇴가 덜 발생하는 것으로 추정된다.5 Fig. 2의 결과에서 수상 직후에 환측과 반대측의 전방깊이의 비대칭성이 고령일수록 더 심해지는 것을 확인할 수 있었는데, 이는 노화에 따른 홍채 근부와 안구 조직 탄력성의 저하 때문으로 판단된다. 흥미로운 점은 수상 1달째 이러한 나이에 따른 비대칭성의 차이가 회복이 되는 것이며, 이러한 회복 정도의 차이가 어떠한 요인에 의한 것인지는 추가적인 연구가 필요하겠다. 최근의 백내장수술 시 인공수정체 도수를 결정하는 공식에서는 전방깊이가 안축장과 각막곡률 이외에 중요한 생체계측치로 사용되고 있는데, 외상성 전방출혈 병력이 있는 환자에서 본 연구와 같은 전방깊이의 변화는 인공수정체 도수 계산의 정확도를 낮추는 결과로도 이어질 수 있겠다.11
본 연구는 후향적으로 진행된 연구로 샘플 크기가 작았으며, 수상 직후 전방깊이에 영향을 줄 수 있는 요소인 산동제 사용을 통제하지 못하였다는 점, 전방깊이에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 수상 전후 앞방각의 후퇴 유무를 확인하지 못 하였다는 점을 제한점으로 꼽을 수 있다. 보통 전방출혈 환자가 외래보다는 응급실로 내원하는 경우가 많으며, 보존적인 약물 치료가 즉시 필요하기에 산동제 사용이 불가피했던 점이 있다. 그러나 산동제 사용으로 인해 증가하는 전방깊이는 평균 0.1 mm 미만으로 알려져 있는데, 본 연구에서 환측이 반대측에 비해 평균적으로 0.27 mm의 전방깊이의 증가를 보였던 것을 고려하면, 산동제의 사용은 본 연구의 결과에 큰 영향을 미치지는 않았을 것으로 사료된다.12 외상성 전방출혈로 내원하는 환자의 특성상 1개월 이후의 추적 관찰을 하기 어려웠던 점과 우각경검사, 전안부빛간섭단층촬영, ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) 등을 통한 앞방각 후퇴 유무를 확인하지 못하였던 점 또한 본 연구의 제한점으로 꼽을 수 있다.
수상 전후 국내에서 전방출혈 환자들을 대상으로 전방깊이의 수상 직후 변화를 분석하였던 연구가 기존에 없었고 해외 연구 또한 소아에 한정되어 있었다는 점에서 본 연구의 의의를 둘 수 있다.13 또한 전방출혈로 인해 예상되는 수정체 홍채면 후방 이동이 실제로 유의한 전방깊이의 증가로 이어진다는 것과 회복 후에도 반대측에 비해 여전히 유의하게 전방깊이가 증가되어 있다는 점을 밝혔다는 점에도 의의가 있다.
결론적으로 전방출혈이 발생한 눈에서 반대측에 비해 수상 직후 유의한 전방깊이의 증가가 관찰되며, 이는 수상 1개월 후 감소하지만, 여전히 반대측에 비해 유의하게 증가되어 있었다(Fig. 3). 수상 직후 환측과 반대측 간 전방깊이의 비대칭은 고령일수록 크게 나타나는 경향을 보였다. 그러나 육안상 전방출혈과 미세전방출혈 간 유의한 전방깊이의 차이는 보이지 않았다. 추후 전방깊이의 차이를 유발하는 요인을 파악하는 추가 연구가 필요할 것으로 보인다.

Comparison of ocular biometry difference between injured eye and contralateral eye at initial and 1 month follow-up examination. (A) Comparison of ACD difference at initial examination and 1 month follow-up examination. (B) Comparison of ACD/AL difference at initial examination and 1 month follow-up examination. ACD = anterior chamber depth; AL = axial length.
*p-value < 0.05.
Notes
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
권윤성 / Yoonsung Kwon
가천대학교 의과대학 길병원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine