 |
 |
| J Korean Ophthalmol Soc > Volume 62(11); 2021 > Article |
|
국문초록
대상과 방법
결과
ABSTRACT
Purpose
Methods
Results
Figure 1.
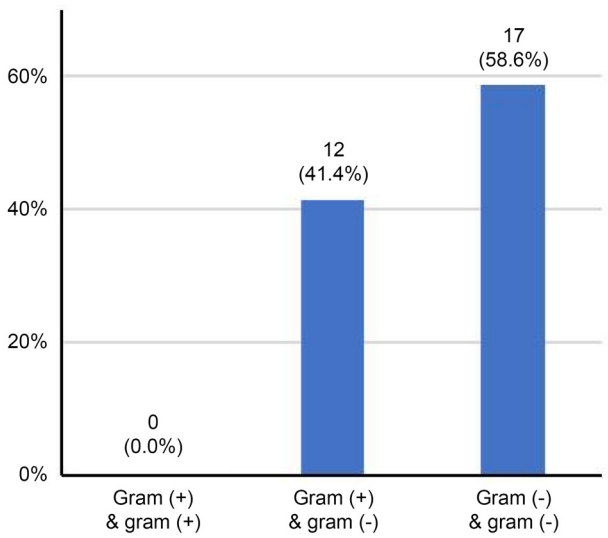
Figure 2.
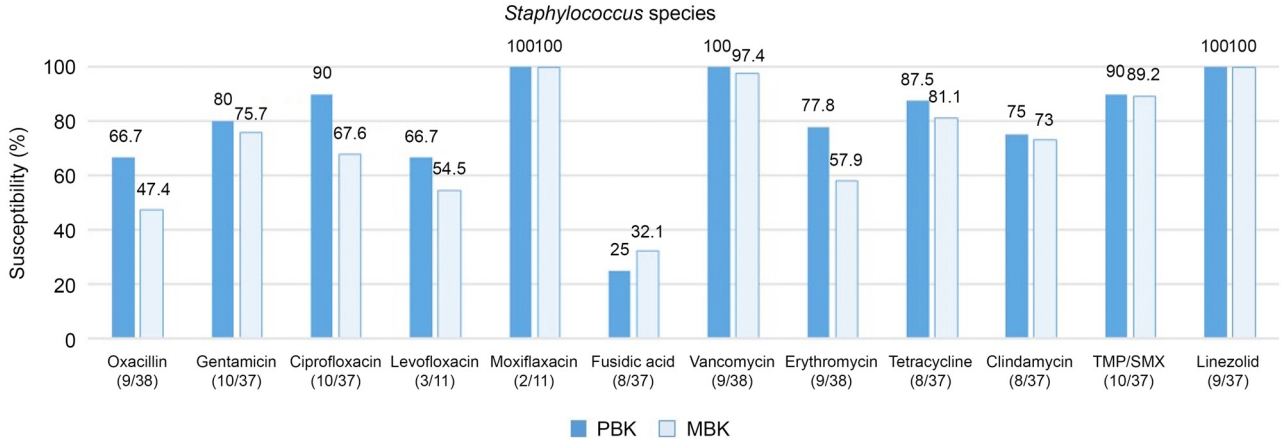
Figure 3.
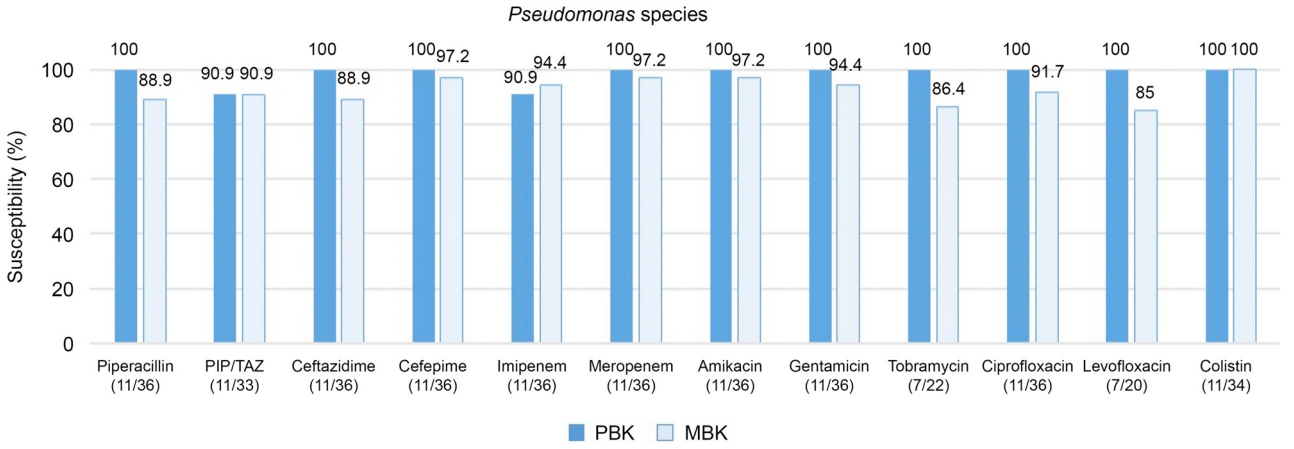
Figure 4.
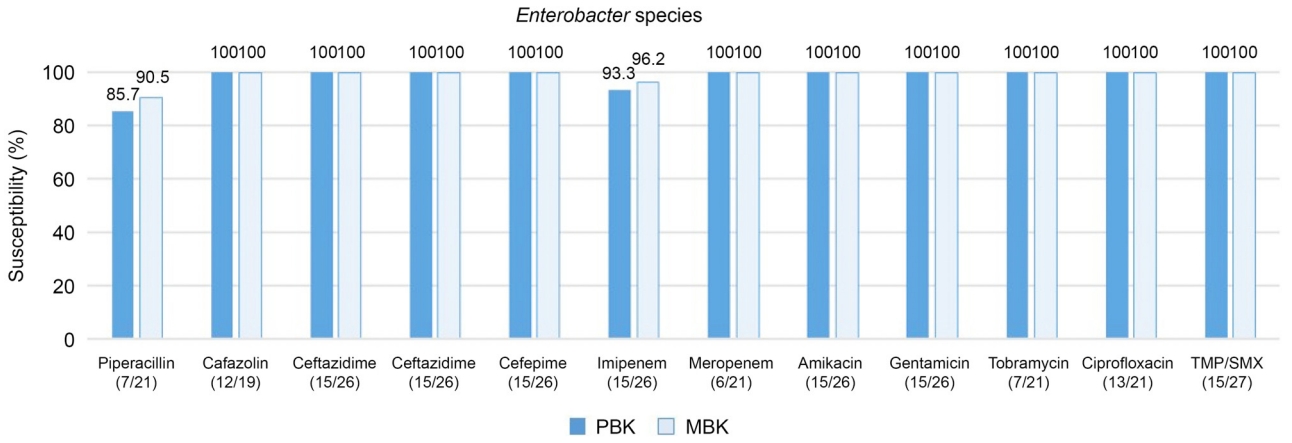
Table 1.
|
PBK* (n = 29) |
MBK (n = 165) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Organism | Value | Organism | Value |
| Gram-positive | 14 (22.6) | Gram-positive | 51 (30.9) |
| Staphylococcus spp. | 10 (16.1) | Staphylococcus spp. | 37 (22.4) |
| Enterococcus spp. | 4 (6.5) | Streptococcus spp. | 8 (4.8) |
| Enterococcus spp. | 6 (3.6) | ||
| Gram-negative | 48 (77.4) | Gram-negative | 114 (69.1) |
| Enterobacter spp. | 15 (24.2) | Pseudomonas spp. | 36 (21.8) |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 11 (17.7) | Enterobacter spp. | 27 (16.4) |
| Serratia spp. | 7 (11.3) | Stenotrophomonas spp. | 21 (12.7) |
| Stenotrophomonas spp. | 6 (9.7) | Serratia spp. | 12 (7.3) |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 4 (6.5) | Acinetobacter spp. | 7 (4.2) |
| Achromobacter spp. | 3 (4.8) | Achromobacter spp. | 2 (1.2) |
| Klebsiella spp. | 1 (1.6) | Delftia spp. | 2 (1.2) |
| Moraxella spp. | 1 (1.6) | Klebsiella spp. | 1 (0.6) |
| Leclercia spp. | 1 (0.6) | ||
| Morganella spp. | 1 (0.6) | ||
| Ochrobactrum spp. | 1 (0.6) | ||
| Pantoea spp. | 1 (0.6) | ||
| Citrobacter spp. | 1 (0.6) | ||
| Total | 62 (100.0) | Total | 165 (100.0) |
Table 2.
| Characteristic | PBK (n = 29) | MBK (n = 165) | p-value (x2-test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male) | 14 (48.3) | 84 (50.9) | 0.794 |
| Age (years) | 48.0 ± 22.4 | 54.3 ± 21.9 | 0.157* |
| ≥60 | 9 (31.0) | 84 (50.9) | 0.048 |
| Age subgroup (years) | |||
| 0-19 | 2 (6.9) | 18 (10.9) | 0.744† |
| 20-39 | 10 (34.5) | 23 (13.9) | 0.013† |
| 40-59 | 8 (27.6) | 40 (24.2) | 0.700 |
| 60-79 | 5 (17.2) | 74 (44.8) | 0.007† |
| ≥80 | 4 (13.8) | 10 (6.1) | 0.233† |
| Right eye | 15 (51.7) | 100 (60.6) | 0.369 |
| Urban residency | 20 (69.0) | 86 (52.1) | 0.093 |
| Symptom duration (days)‡ | 4.7 ± 5.4 | 8.0 ± 8.5 | 0.009* |
| >7 days | 8 (27.6) | 69 (41.8) | 0.149 |
| Duration of hospitalization (days) | 9.6 ± 4.9 | 10.0 ± 5.1 | 0.710* |
| Seasonal distribution | |||
| Spring (Mar-May) | 10 (34.5) | 50 (30.3) | 0.653 |
| Summer (Jun-Aug) | 12 (41.4) | 35 (21.2) | 0.019 |
| Autumn (Sep-Nov) | 5 (17.2) | 46 (27.9) | 0.263† |
| Winter (Dec-Feb) | 2 (6.9) | 34 (20.6) | 0.118† |
Table 3.
| Characteristic | PBK (n = 29) | MBK (n = 165) | p-value (x2-test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Predisposing factor* | |||
| Corneal trauma | 15 (51.7) | 98 (59.4) | 0.440 |
| Contact-lens wear | 10 (34.5) | 29 (17.6) | 0.036 |
| Previous OSD | 7 (24.1) | 45 (27.3) | 0.725 |
| Previous ocular surgery | 3 (10.3) | 33 (20.0) | 0.302† |
| Prior topical steroid use | 5 (17.2) | 29 (17.6) | 1.000† |
| Use of glaucoma eye drops | 2 (6.9) | 5 (3.0) | 0.281† |
| Systemic disease | 4 (13.8) | 51 (30.9) | 0.074† |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 (0) | 20 (12.1) | 0.048† |
| Hypertension | 4 (13.8) | 36 (21.8) | 0.456† |
| No apparent cause | 2 (6.9) | 25 (15.2) | 0.382† |
Table 4.
| PBK (n = 29) | MBK (n = 165) | p-value (x2-test) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristic | |||
| Central lesion* | 17 (58.6) | 93 (56.4) | 0.821 |
| Stromal infiltrate | |||
| Round | 22 (75.9) | 114 (69.1) | 0.463 |
| Others† | 7 (24.1) | 54 (30.9) | 0.417‡ |
| Deep infiltration | 2 (6.9) | 20 (12.1) | 0.539‡ |
| Epithelial defect size (≥5 mm2) | 10 (34.5) | 78 (47.3) | 0.202 |
| Endothelial plaque | 2 (6.9) | 13 (7.9) | 1.000‡ |
| Hypopyon | 7 (24.1) | 41 (24.8) | 0.935 |
| Presenting BCVA (logMAR)§Π | 1.27 ± 1.01 | 1.42 ± 1.05 | 0.460# |
| <0.1 (Snellen) | 16 (55.2) | 86 (52.8) | 0.810 |
| Treatment outcome | |||
| Epithelial healing time (≥10 days)¶ | 16 (57.1) | 98 (62.8) | 0.569 |
| Final BCVA (logMAR)∏** | 0.58 ± 0.96 | 0.87 ± 1.07 | 0.209# |
| <0.1 (Snellen) | 4 (15.4) | 44 (28.9) | 0.231‡ |
| Decreased BCVA** | 1 (3.8) | 14 (9.2) | 0.701‡ |
| Clinical outcome**†† | |||
| Good | 20 (76.9) | 98 (64.5) | 0.215 |
| Poor | 6 (23.1) | 54 (35.5) |
Values are presented as number (%) or mean ± standard deviation.
PBK = polymicrobial bacterial keratitis; MBK = monomicrobial bacterial keratitis; BCVA = best-corrected visual acuity; logMAR = logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution.
Π hand motions, light perception (LP), and no LP were assigned values of 2.3, 2.6, and 2.9, respectively (Botelho et al. [51]);
†† clinical outcomes were assessed at final visit or at the completion of treatment and classified by modifying the criteria defined by Green et al. [6], poor clinical outcome was defined as final BCVA worse than 6/60, decreased VA during treatment, complications, or requiring surgical intervention.
Table 5.
| Characteristic | PBK (n = 29) | MBK (n = 165) | p-value (x2-test) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical topical treatment | |||
| Levofloxacin | 0 (0) | 11 (6.7) | 0.375* |
| Gatifloxacin | 3 (10.3) | 20 (12.1) | 1.000* |
| Moxifloxacin | 20 (69.0) | 101 (61.2) | 0.427 |
| Fortified tobramycin | 26 (89.7) | 138 (83.6) | 0.580* |
| Fortified ceftazidime | 16 (55.2) | 71 (43.0) | 0.225 |
| Fortified cefamandole | 12 (41.4) | 73 (44.2) | 0.774 |
| Fortified vancomycin | 1 (3.4) | 3 (1.8) | 0.480* |
| Surgical treatment | 1 (3.4) | 21 (12.7) | 0.209* |
| AMT | 1 (3.4) | 16 (9.7) | 0.477* |
| Tarsorrhaphy | 0 (0) | 3 (1.8) | 1.000* |
| Penetrating keratoplasty | 0 (0) | 1 (0.6) | 1.000* |
| Evisceration | 0 (0) | 1 (0.6) | 1.000* |
Table 6.
| Variable |
Total group (n = 178)† |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence of poor clinical outcome (%) | Z-score‡ | p-value | |
| Age (≥60 years:<60 years) | 48.9:18.9 | 4.218 | <0.001 |
| Previous OSD (+):(-) | 59.6:24.4 | 4.361 | <0.001 |
| Previous ocular surgery (+):(-) | 58.3:27.5 | 3.490 | <0.001 |
| Prior steroid use (+):(-) | 46.9:30.8 | 1.735 | 0.083 |
| Symptom duration (≥3 days:<3 days) | 39.4:19.6 | 2.515 | 0.011 |
| Presenting BCVA (<0.1:≥0.1, Snellen) | 54.7:9.6 | 6.332 | <0.001 |
| Corneal lesion (central:peripheral) | 44.2:18.9 | 3.511 | <0.001 |
| ED size (≥5 mm2:<5 mm2) | 51.2:18.8 | 4.555 | <0.001 |
| Stromal infiltration (deep:superficial) | 60.0:30.4 | 2.633 | 0.008 |
| Hypopyon (+):(-) | 60.5:25.2 | 4.250 | <0.001 |
| PBK:MBK | 23.1:35.5 | -1.237 | 0.215 |
OSD = ocular surface disease; BCVA = best-corrected visual acuity; ED = epithelial defect; PBK = polymicrobial bacterial keratitis; MBK = monomicrobial bacterial keratitis.
* Clinical outcomes were assessed at final visit or at the completion of treatment and classified by modifying the criteria defined by Green et al. [6], poor clinical outcome was defined as final BCVA worse than 6/60, decreased VA during treatment, complications, or requiring surgical intervention;
‡ a two-proportion Z-test was used to test for a difference between two population proportions. The value of the Z-score for a factor indicates how far away from the mean value of the normal population, as a multiple of the standard deviation. For each variable, the positive direction of the Z-score was defined based on the first of the two independent variable conditions. The Z-scores for each confidence levels of 95%, 99% and 99.9% are ± 1.96, ± 2.58 and ± 3.29, respectively (Hazra [52]).
REFERENCES
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 2,132 View
- 74 Download
- Related articles
-
Clinical Analysis of Bacterial Keratitis According to Culture Positivity.2019 November;60(11)
A Report of Five Cases of Mixed Candida and Bacterial Keratitis.2013 May;54(5)
Clinical Analysis of Infectious Keratitis after LASIK.2007 February;48(2)




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print



