7번 염색체 장완 미세결실 환아에서 나타난 안과적 이상 2예
Two Cases of Ocular Manifestations in Patients with Microdeletion of the Chromosome 7 Long Arm
Article information
Abstract
목적
7q 염색체 미세결실 환아에서 나타난 안과적 증상 2예를 보고하고자 한다.
증례요약
(증례 1) 생후 64일 남자 환아가 DNA 미세배열 비교유전자보합법과 형광제자리부합법에서 7번 염색체의 미세결실(7q36.2q36.3 deletion)이 발견되어 안과적 평가를 위해 내원하였다. 안저검사에서 양안 시신경유두 저형성, 우안 망막출혈을 동반한 미숙아망막병증이 관찰되었다. 생후 24개월경에는 간헐외사시 및 양안의 굴절부등이 발견되어 안경착용을 시작하였다. (증례 2) 만 3세의 남아가 뇌성마비 및 발달지연으로 재활치료하던 중 눈의 초점이 잘 맞지 않는 증상이 발견되어 안과로 의뢰되었다. 안저검사 결과 양안 시신경유두함몰비가 증가되어 있었고, 섬광 시유발전위검사에서 양안 p100 지연 소견을 보였으며, 원거리 40프리즘디옵터의 외사시가 관찰되었다. DNA 검사에서 환아의 7번 염색체 장완의 미세결실(7q35 microdeletion) 및 CNTNAP2 유전자 소실이 확인되었다.
결론
안구발달에 관여하는 유전자 이상이 발견되는 경우, 안과적 이상을 조기에 발견하고 적절한 치료를 함으로써 정상적인 시기능 발달이 가능하도록 해야 할 것이다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
We report ocular manifestations in two patients with 7q microdeletion.
Case summary
(Case 1) A 62-day-old male infant was admitted to the ophthalmology outpatient department for ocular examination after being diagnosed with microdeletion of chromosome seven (7q36.2q36.3 deletion) in DNA microarray comparative genomic hybridization (DNA microarray CGH) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) tests. Fundus examination showed optic disc hypoplasia in both eyes and retinopathy of prematurity, accompanied by retinal hemorrhage in his right eye. Around the age of 24 months, the patient was diagnosed with intermittent exotropia with anisometropia and was prescribed spectacles. (Case 2) A 3-year-old male infant was referred to the ophthalmology clinic to evaluate poor fixation, which was found during rehabilitation therapy for cerebral palsy and developmental delay. Fundus examination showed an increased cup/disc ratio bilaterally. A flash visual evoked potential test indicated a decrease in amplitude in his right eye. Intermittent exotropia of forty prism diopters was observed. DNA microarray CGH and FISH tests performed at another hospital revealed microdeletion of chromosome seven (7q35 microdeletion) and CNTNAP2 gene loss.
Conclusions
When genetic anomalies associated with ocular development are identified, it is necessary to detect the ophthalmic abnormalities early and provide the appropriate treatment to allow for the development of normal visual function.
안구는 가장 정교하고 섬세한 기관 중 하나로, 각막, 홍채, 수정체, 망막 등은 각각 발생학적 기원이 서로 다르기 때문에, 다양한 유전자가 안구의 발생에 관여한다. 최근 유전자 분석 방법이 발전하면서 선천성 안질환을 일으킬 수 있는 유전자들을 발견하기 위한 많은 연구들이 진행되고 있다[1]. 대표적인 유전성 안질환으로 잘 알려진 각막 이영양증은 아형별로 5q31, 16q21, 17q12 등 다양한 유전자좌(locus)의 이상에 의해 발현되며[2], 망막색소상피변성증은 40개 이상의 유전자 변이에 의해 발현될 수 있다고 보고되고 있다[3]. 또한 G protein-coupled receptor 143의 변이는 눈백색증(ocular albinism)을 야기하여, 망막저색소(fundus hypopigmentation), 중심오목저형성(foveal hypoplasia), 눈떨림 등 다양한 증상을 야기할 수 있다[4]. 이처럼 하나의 안질환에 다양한 유전자가 관여하기도 하고, 하나의 유전자가 두 종류 이상의 안구 이상에 관여하기도 하므로 유전자 연구를 위해 고도의 기술이 필요하며, 차세대 염기서열 분석 기술의 발달로 다양한 유전성 안질환의 진단과 치료에 유전자 분석기술이 적용되고 있다[1].
선천성 안질환을 나타낼 수 있는 다양한 유전자 중 7번 염색체 장완(7q) 이상에 의해 발현된 안구 이상에 대한 보고는 드물다. 해외에서 7q36 부위에 미세결실에 의하여 발생한 소안구증 및 소각막증, 시신경유두 저형성증 등이 보고된 바가 있으나[5,6], 아직 국내에는 보고된 바가 없어, 이에 대한 두 증례를 보고하고자 한다.
증례보고
증례 1
생후 65일의 남아가 출생 후 12일에 시행한 DNA 미세배열 비교유전자보합법(DNA microarray comparative genomic hybridization, DNA microarray CGH)과 형광제자리부합법(fluorescence in situ hybridization, FISH) 검사에서 7q36.2q36.3 미세결실 및 Sonic hedgehog (SHH) 유전자 소실이 발견되어 안과적 평가를 위하여 의뢰되었다. 환아는 재태연령 36주 4일, 체중 2.46 kg으로 제왕절개술을 통하여 출생하였으며, 주산기 문제는 없었다.
안저검사에서 양안 시신경유두의 정상적인 함몰이 관찰되지 않았고, 우안 망막앞출혈이 동반된 zone 2의 stage 2 미숙아망막병증(retinopathy of prematurity, ROP)이 확인되었으며(Fig. 1A), 이후 ROP는 자연 소실되어 이에 대한 치료는 시행하지 않았다. 생후 24개월에 시행한 눈운동검사에서 원거리 20 prism diopters (PD)의 외편위가 관찰되었고, 조절마비굴절검사에서 우안 구면도수 -3.0 diopter (D), 난시도수 -0.5 D, 좌안 구면도수 +0.75 D, 난시도수 -0.25 D로 측정되어, 부등시성 약시치료를 위해 안경을 처방하였다. 발달지연으로 시표를 이용한 시력검사는 불가능하였으며, 좌안에 비하여 우안의 주시 및 추종(fix and follow)이 불량하였다. 섬광 시유발전위검사(flash visual evoked potential, flash VEP)에서 양안의 진폭 감소 및 P100 지연이 관찰되었으며(Fig. 1B), 망막전위도검사 및 뇌자기공명검사(brain magnetic resonance imaging, brain MRI)에는 특이 소견이 관찰되지 않았다.
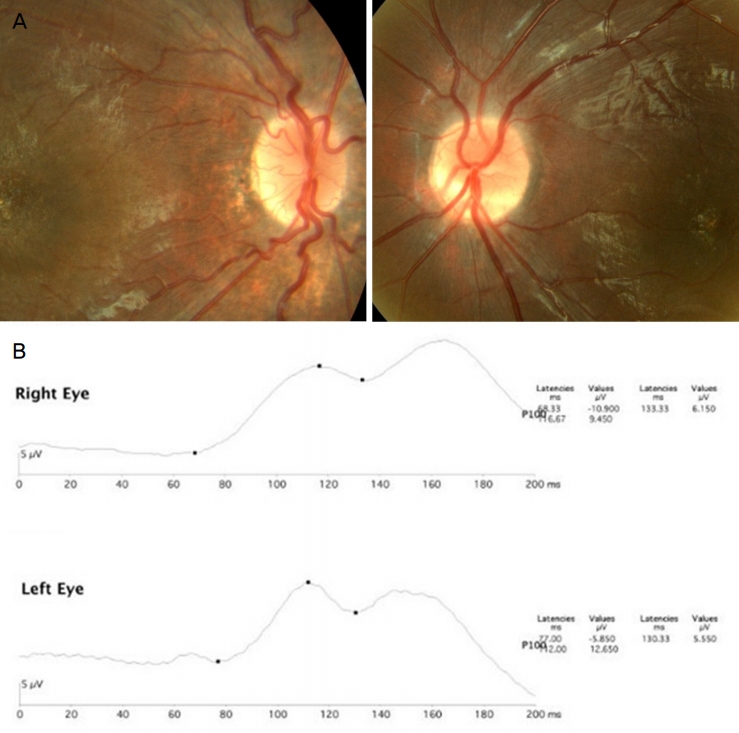
Photographs of case one. (A) Fundus photos of case one shows suspected optic disc hypoplasia in both eyes. Zone two stage two retinopathy of prematurity has self-regressed after 2 years of follow-up in fundus exams. (B) The flash visual evoked potential test results show decrease in amplitude and delay of the P100 latency in both eyes.
증례 2
만 3세의 남아가 발달지연으로 재활 치료를 받던 중 눈의 초점이 맞지 않는 증상이 발견되어 안과로 의뢰되었다. 환아는 생후 8개월경 발달지연, 뇌성마비(cerebral palsy) 진단을 받았으며, 만 2세경 시행한 brain MRI, SMN1/SMN2 유전자 이상검사 및 프래더-윌리 증후군 유전자 선별검사, 뮤코다당질축적증(mucopolysaccharidosis) 선별검사, 뇌파검사에서 특이 소견은 발견되지 않아 DNA microarray CGH 및 FISH 검사를 시행하였고, 7q35 미세결실 및 CNTNAP2 유전자 소실 소견이 발견되었으며, 부모 세대에서는 변이가 발견되지 않았다. 초진 당시 시력검사는 협조가 되지 않았으나 주시와 추종은 양호하였고, 안저검사에서 양안의 시신경유두함몰비가 증가되어 있었으며, 유두황반신경섬유다발의 결손이 보였다(Fig. 2A). 눈 운동검사에서 35 PD의 외편위가 관찰되었고 눈떨림은 동반되지 않았으며, 조절마비굴절검사에서 양안 구면도수 +1.0 D로 측정되었다. flash VEP에서 우안 진폭 감소 및 양안 P100 지연 소견이 확인되었다(Fig 2B).
고 찰
7번 염색체 장완의 유전자 이상으로 발생하는 선천성 안구이상에 대해서는 아직 연구된 바가 많지 않다. 현재까지 알려진 바에 따르면, 7q32.1 유전자좌 이상에 의해 상염색체 우성 망막색소변성증이 일어날 수 있다고 보고된 바가 있고[7], 같은 유전자좌 이상에 의해 레버선천흑암시(leber congenital amaurosis)가 발병한 증례가 보고되기도 하였다[8]. 또한7q33-q36.1의 이상은 선천성 백내장과 관련성이 있으며[9], 7q35-7q36 유전자이상에 의해 색소분산증후군이 나타날 수 있다고 하였다[10]. 7q36에 있는 SHH 유전자는 신경전구체의 확산 및 신경축삭의 성장을 조절하여 중추신경계의 발달에 중요한 역할을 하여, 이 부위에 이상이 있는 경우 전전뇌증(holopresencephaly)부터 소안구증, 무안구증 등 다양한 양상의 안구결손증이 나타날 수 있다고 보고되었다[5,11].
본 연구에서는 7번 염색체 장완의 끝 부분인 7q36.2q36.3 (증례 1) 및 7q35 (증례 2) 유전자좌의 미세결손이 있는 두 환아를 보고하였고, 공통적으로 시신경유두이상, 외사시, 시유발전위검사에서의 P100 지연 소견이 관찰되었으며, 정신지체 및 발달지연 외의 신체적 기형 또는 중추신경계 결손은 동반하지 않았다.
증례1의 7q36.2q36.3 결손의 경우 국외에서 몇 차례 보고된 바가 있는 7q36 결손 증후군의 한 형태로, 이 증후군은 발달장애, 천골기형, 전전뇌증 등을 동반하는 특징이 있다. 전전뇌증은 대뇌와 전뇌가 중추신경 발달과정에서 완전히 분리되지 않는 것을 말하는데, 1984년 Berry et al [12]에 의해 처음 유전에 의한 전전뇌증이 보고되었으며, 현재 그 원인 중 가장 대표적인 것이 7q36.3 유전자좌에 위치한 SHH 유전자의 돌연변이에 의한 것으로 알려져 있다. 전전뇌증은 구개열, 치아결손 등의 안면기형, 소뇌증 등의 중추신경 장애, 홍채결손, 시신경결손 등의 안구이상 등 다양한 표현형을 함께 동반하며[6], 이전 보고에서 안면기형과 시신경유두위축 두 가지가 동반된 경우가 있었다[13]. 그러나 7q36 결손 환아에서 전뇌이상 및 안면기형, 수족부기형 등의 선천이상을 동반하지 않고, 눈의 이상만 동반한 경우는 아직 보고된 바가 없다. 본 연구의 사례처럼 7q36.2q36.3내의 SHH 결손 정도에 따라 안구의 이상만 나타날 가능성이 있는 것으로 보인다.
증례 2에서 나타난 7q35 유전자좌 미세결손의 경우 GPDS1, PDS1 유전자 이상이 있는 경우 색소분산증후군이 유발되며[10], GLC1F 유전자 이상이 있는 경우 원발개방각녹내장 발생과 관련성이 보고된 바가 있다[14]. 이러한 녹내장 관련 유전자의 위치(7:143,400,000)와 본 증례(146,573,755-146,889,835)는 다른 부위의 미세결손이며, 본 환아의 이측망막신경섬유층(retinal nerve fiber layer, RNFL) 결손은 대뇌의 이상에서 기인하였을 가능성이 높으나, 향후 시신경 및 RNFL의 변화에 대한 정기 관찰이 필요할 것이다.
유전질환에서 흔히 동반되는 안과적 이상으로는 시신경 이상, 백내장, 안검하수, 사시, 굴절이상 등이 보고되고 있다[3,4,7-9]. 백내장, 안검하수처럼 시자극 차단이 약시로 이어질 위험이 있을 경우 조기에 수술이 필요하고, 사시, 굴절이상 등 약시를 유발하는 요소가 발견될 경우 안경착용 및 가림치료 또는 사시수술이 필요할 수 있다. 또한 시신경, 망막 등에 구조적인 문제가 있더라도 안경을 통한 굴절이상 교정으로 선명한 상을 유도하고, 고식적인 약시치료를 할 경우 시력호전 효과가 있다고 알려져 있어[15], 안과적 이상을 조기에 발견할 경우 최종적인 시기능을 개선하는 데에 도움이 될 수 있다. 본 증례에서 증례 1 환아의 경우 부등시성 약시가 의심되어 조기에 안경착용 및 가림치료를 시작하였고, 증례 2 환아의 경우 시신경유두함몰비의 증가 및 외사시를 조기에 발견하여 추후 시야, 시력, 양안시기능 등의 시기능 저하에 대한 주기적 경과 관찰을 계획할 수 있었다.
최근 DNA microarray CGH 등 유전자 분석 기술의 발달과 유전자 지도에 대한 정보가 축적되면서, 선천성 질환에 대한 조기 진단이 보다 정확해지고 있다. 소아 환자의 특성상, 특히 발달지연 및 지적장애를 가지고 있는 환아들의 경우 시력 증상을 적절히 표현하지 못하므로, 영구적인 시력 손상을 일으킬 수 있는 문제를 발견하지 못하고 방치되는 경우가 있다. 따라서 유전자 이상을 진단받았을 때 안과적 평가를 통해 약시를 유발하는 눈의 이상을 조기에 발견하고, 적절한 처치를 함으로써 선천성 질환이 있는 환아의 시기능 개선에 도움을 줄 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
김상윤 / Sang Yoon Kim
부산대학교 의과대학 양산부산대학교병원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine

