선천저감마글로불린혈증 환아에서 발생한 사이질각막염
Stromal Keratitis in a Patient with Congenital Hypogammaglobulinemia
Article information
Abstract
목적
선천저감마글로불린혈증 환아에서 사이질각막염을 경험하여 보고하고자 한다.
증례요약
15세 남자가 우안 시력저하로 내원하였다. 환아는 생후 16개월에 선천저감마글로불린혈증을 진단받고 정기적으로 면역글로불린을 투여 받고 있었다. 우안 최대교정시력 0.02, 안압 11 mmHg였고 전안부검사상 중심부와 주변부 각막사이질의 침윤과 얇아진 소견이 관찰되었으나 상피결손은 없었다. 급성사이질각막염으로 진단하고 1% Prednisolone acetate, 5% NaCl, Levofloxacin 점안액으로 치료를 시작하였다. 전신검사상에서 혈청 immunoglubulin G (IgG) 수치가 328.9 mg/dL로 3개월 전인 434.8 mg/dL에 비해 감소되어 있었다. 안약 점안 후에도 병변의 호전은 없었으나, 면역글로불린 투여 후 IgG 수치가 394.4 mg/dL로 증가하며 각막침윤이 감소하였다. 이후 IgG 수치는 480-530 mg/dL로 유지되었고 최대교정시력은 0.15, 각막두께는 330 μm로 측정되었으며 각막병변의 재발과 악화는 없었다.
결론
선천저감마글로불린혈증 환자에서 혈청 IgG 수치가 저하되며 발생한 사이질각막염에서 면역글로불린 투여로 호전되는 소견을 관찰하여 이를 보고한다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
We report a case of stromal keratitis in a patient with congenital hypogammaglobulinemia.
Case summary
A 15-year-old boy presented with decreased visual acuity in the right eye. He had been diagnosed with congenital hypogammaglobulinemia at about 16 months of age and had received regular doses of intravenous immunoglobulin. The best-corrected visual acuity of the right eye was 0.02 and the intraocular pressure 11 mmHg. On anterior segment examination, thinning combined with stromal infiltration of the paracentral cornea was evident, but no epithelial defect was apparent. We scheduled detailed systemic examinations and laboratory investigations to rule out infectious keratitis. His serum immunoglubulin G (IgG) level was 328.9 mg/dL, thus less than that 3 months priorly (434.8 mg/dL). The lesion did not improve after prescription of topical antibiotics and steroid. The serum IgG level gradually increased to 394.4 mg/dL after immunoglobulin administration, and the corneal infiltration gradually decreased. After 5 months of treatment, the serum IgG levels ranged between 480 and 530 mg/dL; we noted no recurrence or worsening of the corneal lesion.
Conclusions
We report a case of stromal keratitis in a patient with congenital hypogammaglobulinemia; we prescribed intravenous immunoglobulin.
사이질각막염(stromal keratitis)은 각막 사이질의 염증반응과 궤양성 병변을 의미하며, 각막염이 회복된 이후에도 각막혼탁 및 얇아짐을 남길 수 있어 영구적인 시력저하를 일으키는 원인이 된다. 매독이나 헤르페스 바이러스 등의 원인균에 의한 감염이나 염증 반응에 의한 사이질각막염이 흔하며, 자가면역질환에 동반된 면역반응에 의해서도 사이질각막염이 발생할 수 있다. 사이질각막염의 치료로는 감염에 의한 경우 감염 원인에 따른 전신 및 점안 항생제를 투여하고, 면역 반응에 의한 각막염은 국소 또는 점안 스테로이드를 사용한다[1,2].
면역 결핍증은 면역기능이 정상인 사람이 질병으로 인하여 면역기능에 결함이 생긴 2차 면역결핍과, 선천적으로 발생하는 1차 면역결핍증으로 나눌 수 있다. 이 중에서 1차 면역결핍증은 1만명 중 한 명의 빈도로 발생하며 결함이 있는 면역계에 따라 B세포, T세포, 보체계, 식세포 이상으로 분류된다. 이 중에서 저감마글로불린혈증(hypogammaglobulinemia)은 B세포 또는 체액면역결핍증에 해당하는 질환으로 반성우전, 상염색체 열성유전 또는 산발성으로 발생한다. 임상양상으로는 반복적인 세균감염으로 인한 만성 부비동염, 중이염, 폐렴, 기관지 확장증, 세균성 설사 등을 보일 수 있으며, 25%에서는 비장비대가 관찰된다. 그 외에도 가슴샘종, 용혈빈혈, 가성 림프종, 폐, 간, 비장에서 비건락성 육아종증이 관찰되기도 하며 자가면역질환이 흔하여 특발성 관절염이 동반되는 경우가 있다[3-5]. 체액성면역결핍증에 동반된 안과 질환으로는 망막혈관염, 시신경염, 포도막염, 각막천공 등이 보고되었으나, 사이질각막염의 임상형태를 보인 환자에 대한 보고는 없었다[6-9]. 저자들은 선천저감마글로불린혈증 환자에서 사이질각막염의 임상양상을 보인 환자에서, 정맥 면역글로불린 주사를 통해 호전된 증례를 경험하였기에 이를 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하고자 한다.
증례보고
15세 남자 환아가 1개월 전부터 진행되는 우안의 시력저하와 충혈을 주소로 내원하였다. 평소 양안 시력 차이는 없었으며, 외상이나 수술의 과거력도 없었다. 우안의 시력저하는 1달 전부터 서서히 진행하였으며 안구통증이나 분비물은 동반되지 않았다. 환아는 생후 16개월경 선천저감마글로불린혈증을 진단받고, 1달 간격으로 면역글로불린을 정맥으로 투약하며 경과 관찰 중이었으며, 평소 혈중 immunoglubulin G (IgG) 농도는 400-500 mg/dL로 유지되었다고 한다. 초진 시 우안의 최대교정시력은 0.02, 좌안은 1.0으로 측정되었으며, 안압은 우안 11 mmHg, 좌안 14 mmHg였다. 세극등검사에서는 우안 중심 각막에 상피결손이 없이 사이질 침윤이 보였으며, 병변 부위에는 각막이 얇아져 있었으나 돌출되지는 않았다. 각막 중심부 병변 부위 주위로는 부종이 관찰되었으나 그 외에 주변부 각막에는 특이 소견이 없었으며, 경도의 결막 충혈을 보였다(Fig. 1). 전안부 빛간섭단층촬영(Spectralis®, Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany)에서는 각막의 사이질이 얇아진 소견이 관찰되었고, 가장 얇은 부위의 전체 각막두께는 207 μm로 측정되었다(Fig. 1). 각막내피침착물이나 전방의 염증은 관찰되지 않았으며, 수정체와 유리체 그리고 안저검사에서는 특이 소견이 관찰되지 않았다. 감염성 각막염을 배제하기 위해 병변 부위를 찰과 후에 그람염색과 배양검사, 헤르페스 바이러스 중합효소연쇄반응 검사를 실시하였다. 이후, 우안에 Levofloxacin (Cravit® Ophthalmic solution, Santen, Osaka, Japan), 1% Prednisolone acetate (PRED FORTE®, Allergan Inc., Irvine, CA, USA), 5% NaCl (Muro128®, Bauch & Romb, Rochester, NY, USA) 점안액을 4시간 간격으로 점안하였다. 환아는 주기적인 소아청소년과 진료 및 1달 간격으로 17.5 mg의 면역글로불린을 투약 중이었으며, 2-3개월에 한 번씩 혈액검사로 혈중 IgG 농도를 측정하고 있었다. 내원일로부터 약 2개월 전 시행한 혈중 IgG 농도는 434.8 mg/dL이었으나, 내원 일주일 전 시행한 혈중 IgG 농도는 328.9 mg/dL로 감소한 상태로 혈중 IgG 농도가 지속적으로 감소했음을 유추할 수 있었다. 하지만, 혈중 IgG가 감소할 수 있는 세균이나 바이러스에 의한 감염, 악성 종양, 스테로이드와 같은 약물의 사용, 그리고 신장질환이나 외상 등은 없었다. 혈액검사에서도 백혈구 수치의 상승이나 C-reactive protein 등의 상승 소견도 없었다. 내원 당시 시행한 각막찰과 후 염색과 배양검사 결과는 음성이었으며, 내원 후 2주 동안의 안약 점안에도 각막병변은 호전이 없었다. 이후 소아청소년과에서 정해진 날짜에 면역글로불린을 정맥 투여 후에 혈중 IgG 농도는 394.4 mg/dL로 증가하였고, 이후 1주일이 지난 후부터 각막사이질의 침윤과 염증은 호전되기 시작하였다. 이후 안약은 서서히 중단하였으며, 3개월 후에 우안 최대교정시력은 0.06으로 향상되었고, 각막 사이질 침윤도 감소하였다. 5개월 후에는 혈중 IgG 농도는 481.9 mg/dL로 증가하였고, 우안 최대교정시력은 0.15로 호전되었고, 각막 중심부에 혼탁이 남았지만, 사이질 침윤과 주변부 부종도 호전되었다. 빛간섭단층촬영에서 각막두께는 330 μm로 측정되었으며, 각막이 가장 얇아진 부위가 약간 돌출된 소견이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2). 이후 주기적으로 검사한 혈중 IgG 농도는 480-530 mg/dL를 유지하였으며(Fig. 3), 각막병변 또한 1년 이상 추적 관찰 시 진행 또는 재발이 없었다.
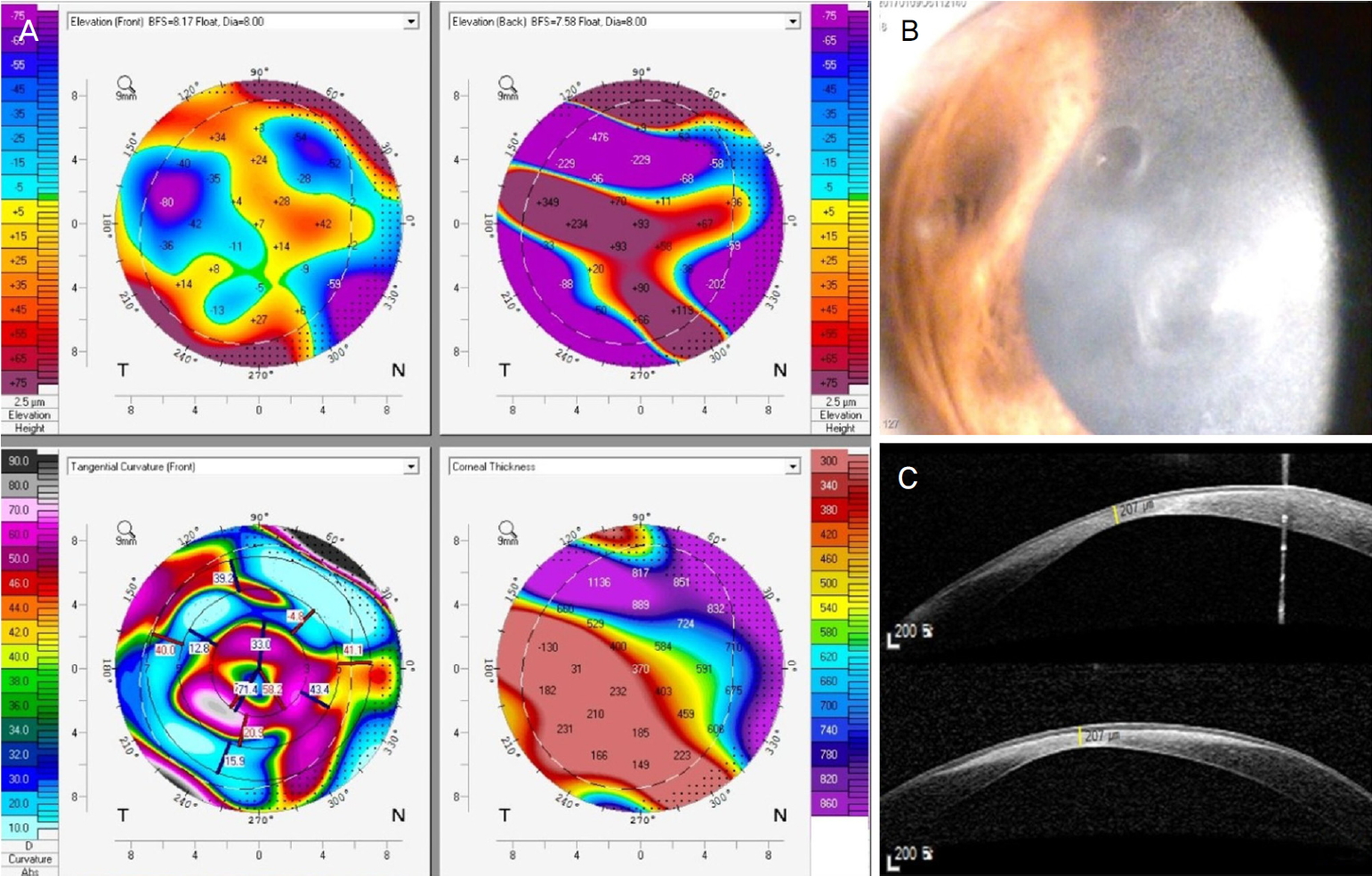
Corneal topography, anterior segment photography and anterior segment optical coherence tomography at initial visit. (A) Topography showed corneal thinning. (B) Anterior segment photography showed paracentral cornea stromal infiltration without overlying epithelial defect. (C) Anterior segment optical coherence tomography showed corneal thinning and the thinnest corneal thickness was 207 μm.

Corneal topography, anterior segment photography, and anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) at 5 months later after initial visit. (A) Topography showed reduced corneal thinning and edema. (B) The corneal opacity remained in the paracentral area (C) and AS-OCT showed no more progression of corneal thinning (330 μm).
고 찰
사이질각막염은 감염 또는 면역 반응에 의해 발생한다고 알려져 있으며, 각막 사이질로 대식세포 등 면역세포가 침윤이 되고, 괴사된 각막 간질세포 등에 의해 육아종성 반응을 일으켜 병변이 진행하게 된다. 사이질각막염의 원인으로는 매독균이나 헤르페스바이러스 등의 감염뿐만 아니라, 베체트 병과 같은 자가면역질환에서도 발생할 수 있으며, 코간 증후군에 동반된 사이질 각막염이나 전신결핵에 동반된 사이질 각막염 등도 보고되고 있다[10,11].
저감마글로불린혈증은 체액 면역의 결핍으로 항체의 생성과 분비의 장애로 인하여 항체가 결핍되어있는 상태이다. 저감마글로불린혈증 환자에서 면역결핍과 동반되어 나타나는 안과적 합병증으로는 Pseudomonas aeruginosa와 같은 세균성 감염과 함께 Cytomegalovirus나 Varicella Zoster virus와 같은 바이러스 감염이 드물지 않게 보고되고 있다. 하지만 이런 감염 질환 뿐만 아니라 망막혈관염이나 망막정맥폐쇄, 그리고 시신경염 등의 면역 반응에 의한 질환이 발생하여 스테로이드 등으로 치료한 증례가 보고된 바가 있다[6,7,12]. 또한, 저감마글로불린혈증에서 보고된 각막 합병증으로는 양안 사이질각막염 소견이 보여 점안 스테로이드 안약으로 치료 중 각막천공이 발생하여 수술적 치료를 시행한 증례와 범저감마글로불린혈증에서 동종골수이식을 시행한 환아에서 발생한 사이질각막염을 치료한 증례가 보고된 바가 있다[9,13].
저감마글로불린혈증에서 각막염이 발생하는 기전은 대개 염증에 의한 것이라고 보고되고 있으며, 면역반응에 의한 각막염은 오히려 저감마글로불린혈증을 치료하기 위해 정맥으로 글로불린을 주사한 경우에 발생할 수 있다고 한다. 하지만, 본 증례의 경우에는 혈중 IgG 농도가 감소하면서 사이질각막염과 각막이 얇아지는 소견을 보였다. 그리고, 각막찰과나 배양검사에서는 감염 소견이 보이지 않아 스테로이드 등으로 치료를 하였으나 효과가 없이, 면역글로불린을 정맥으로 투여한 후에 혈중 IgG 농도가 상승하면서 사이질각막염과 각막두께가 어느 정도 회복되는 소견을 보였다. 그리고 경과 관찰 중에 혈중 IgG 농도가 일정 범위 내로 유지되면서 병변의 재발이나 악화는 관찰되지 않아 선천저감마글로불린혈증 환자에서 정맥 면역글로불린 투여가 사이질 각막염의 치료와 재발 억제에 효과가 있었던 증례였다. 본 증례의 각막염 발생 기전을 추측하면, 다른 치료의 변화 없이 혈중 IgG가 상승하면서 각막염이 호전된 것을 볼 때, 배양검사에서 양성이 나오지는 않았지만 세균이나 바이러스성 각막궤양 등과 같은 감염 질환이 원인일 가능성이 크다. 실제로 이전 보고에서 저감마글로불린혈증 환자에서 사이질각막염 소견이 있을 때 스테로이드 등의 점안제로만 치료하였을 때 각막천공이 발생한 보고를 참고하면, 혈중 IgG 농도를 측정하여 수치가 감소하였다면 정맥 면역글로불린 주사 치료를 점안 치료와 함께 시행하는 것이 합병증을 예방할 수 있는 방법이라고 생각이 된다. 본 증례에서는 소아청소년과에서 시행한 정맥 면역글로불린 주사 치료 스케쥴 이외 추가적인 주사는 시행하지 않아 각막혼탁이 남게 되었다. 만약, 혈중 IgG 농도가 낮으며 사이질각막염 소견이 있을 때, 추가적인 면역글로불린을 빠른 시일 내에 투여하는 것도 각막혼탁을 줄여 시력예후에 도움이 될 수 있을 것으로 생각이 된다. 결론적으로 저자들은 선천저감마글로불린혈증 환자에서 혈중 IgG 농도의 감소로 발생한 사이질각막염에서 전신적인 면역글로불린 투여로 IgG 농도가 상승되면서 사이질각막염과 각막이 얇아지는 소견이 호전되는 증례를 경험하여 이를 보고하고자 한다.
Notes
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
References
Biography
강현지 / Hyun Ji Kang
경상대학교 의과대학 경상대학교병원 안과학교실
Department of Ophthalmology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine

